How Do Bitcoin Transaction Fees Work
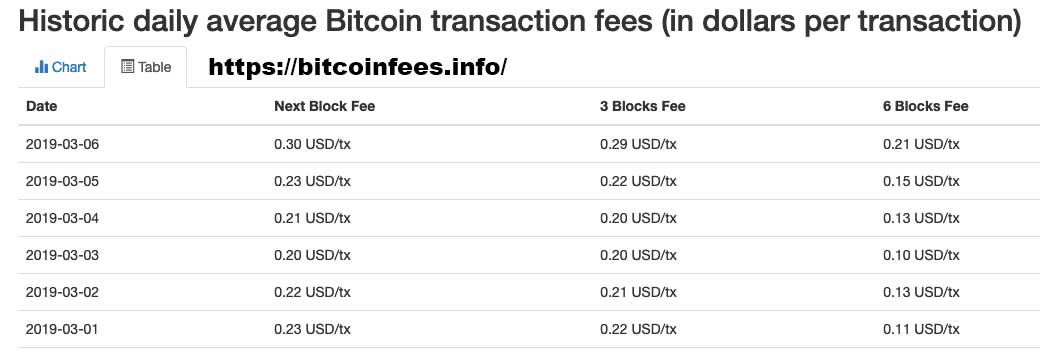
When a user creates a Bitcoin transaction, they have to include a transaction fee to be paid to miners to incentivize miners to add their transaction to the blockchain.
Cryptocurrency is a general name referring to all encrypted decentralized digital currencies like Bitcoin.
Cryptocurrency uses cryptography to create coins and secure transactions. Typically cryptocurrencies are open source with pubic, but encrypted, ledgers of all transactions based on blockchain technology.
There are a number of cryptocurrencies traded on cryptocurrency exchanges, and the growing popularity of cryptocurrency means that despite volatile prices, market caps and values are growing every year.
Popular cryptocurrencies include the original Bitcoin, Ethereum’s Ether, and Litecoin.
Cryptocurrency is legal and taxable in the US, but it isn’t legal tender (you can’t pay your taxes in Bitcoin, it is considered investment property). With that said, due to its infancy and history so far, cryptocurrencies should be invested in and used with their historical volatility in mind.
Click on any of the pages below to learn more about cryptocurrency.
TIP: If you are new to cryptocurrency, check out our guide to cryptocurrency for beginners.

When a user creates a Bitcoin transaction, they have to include a transaction fee to be paid to miners to incentivize miners to add their transaction to the blockchain.
Digital asset is a term that describes any asset in an electronic form. Crypto assets are digital assets that utilize the technology behind cryptocurrencies.
In cryptocurrency sometimes terms get used loosely or one term gets used in place of another. Let’s discuss some crypto semantics.
In cryptocurrency, the term Security Token can either be referring to 1. a cryptocurrency token registered as a security, 2. a digital representation of a traditional security like a stock (a tokenized security), or 3. a cryptographic code used in computer security.
When a coin does a hard fork, two identical blockchains exist until changes to one of the chains is made. To avoid transaction replays (transactions made on one chain being broadcast on the other), at least one chain must implement replay protection (developers of one chain must change the format of transactions to make them unique).
A QR code is a simple, fast, and secure way to share an address when transferring cryptocurrency between two devices.
In Bitcoin, halving is when block rewards for mining are cut in half. Halving happens at regular intervals based on the Bitcoin protocol.
Digital Security Offerings (DSOs) and Security Token Offerings (STOs) are terms that describe “offerings” of digital securities and tokenized securities respectively.

Ethereum 2.0 (ETH) is a term used to describe a series of potential updates to Ethereum to make it more scalable, more secure, and more sustainable.
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT), AKA blockchain and other similar technology, is a way to describe the technology behind distributed databases secured by cryptography and consensus.
By continuing to use the site, you agree to the use of cookies. more information
The cookie settings on this website are set to "allow cookies" to give you the best browsing experience possible. If you continue to use this website without changing your cookie settings or you click "Accept" below then you are consenting to this.