What is a Cryptocurrency Token?
Understanding Cryptocurrency Tokens, ERC-20 Tokens, and Tokenization in Cryptocurrency and in General
The term “token” has a few different meanings in cryptocurrency and in general. We explain the general meaning and describe how tokens work with payment systems and with cryptocurrency specifically.[1][2][3][4]
Short answer: In cryptocurrency, “token” is often used as a synonym for “cryptocurrency.” Often the two terms are combined and the term “cryptocurrency token” is used. Consider, the unit of account on the Bitcoin blockchain is the Bitcoin token, and the united of account on the Ethereum blockchain is the Ethereum token. Cryptocurrencies exist as tokenized data (a type of encrypted data used in both cryptocurrency and computer security in general), therefore cryptocurrencies are often called tokens. That said, sometimes people use the term token to specifically refer to a digital asset that exists on another cryptocurrency’s blockchain (for example OMG is an ERC-20 token on the Ethereum blockchain). With all that covered, a token is just a string of numbers and letters used in types of cryptography like computer security (for example the type of security underlying cryptocurrency technology). Given the many ways tokens related to cryptocurrency, there is a lot to cover below for a full explanation.
What Does the Term “Token” Mean in Cryptocurrency?
Generally speaking, a token is a stand-in for something else. That is true in both cryptocurrency and computer security.

In computer security and cryptocurrency, the term token is generally referring to a cryptographic string of numbers and letters that contains no real data but relates back to real data (that cryptographic code is a “stand-in” for real data). In computer security, this type of token can be called a “security token” (not to be confused with tokenized securities).
In cryptocurrency, more than one aspect of a transaction exists as “tokenized data.” A token might looks something like this: 947153d332beaf39dec6ebae8883bfb84eda47abccccbc2d61436d8d1e81584d.
In cryptocurrency, the term token can be generally referring to either any given “cryptocurrency token” (ex. BTC, ETH, LTC, etc) or it can be referring to a token that exist on another cryptocurrency’s blockchain (ex. ICO tokens on the Ethereum blockchain).
When no other context is given, when discussing cryptocurrency, one should generally assume the term “token” is being used as a synonym for “a cryptocurrency.”
Meanwhile, when “token” is being used to describe a specific type of cryptocurrency, then one should assume it is referring to a crypto that exists on another cryptocurrency’s blockchain like Ethereum’s.
Meanwhile, when discussing computer encryption or computer security, one should assume token describes a string of numbers and letters used in encryption and not a “value token” like Bitcoin (the Bitcoin token is a stand-in for value, just like money is).
With all that in mind, the short answer as to why all the above and more is true is because cryptocurrencies are value tokens that mostly exist as tokenized transaction data stored on blockchains.
In short, a cryptocurrency meant to be used as money relates to the term token in more ways than one.
That is the gist of everything the average person needs to know about tokens, the rest of the page is really about adding detail and clarity to the above.
Did you know? Not only can you tokenize money, for example the Bitcoin token is an example of this, but you can tokenize almost anything. For example, you create a token that represents a piece of real estate or a stock, and then you can trade that token using technologies behind cryptocurrencies (like blockchains and smart contracts).
Different Ways the Term Token is Used in Cryptocurrency
With those general points in mind, the term “token” is used a few different ways in cryptocurrency (some noted above, some not noted yet).
In cryptocurrency:
- The term token is used in a very general sense to describe any digital asset (where Bitcoin is a “cryptocurrency token” and Ether is a “cryptocurrency token”… but even cryptos not meant to be used as money, like the collectable CryptoKitties, still exist as tokens).
- The term token is used to describe a unit of value (I have X Bitcoin tokens). Here it refers to the fact that cryptocurrencies, like the U.S. dollar, are value tokens / currency tokens / token money (they represent value, but aren’t themselves of any inherent value)
- The term token refers to the fact that the creation, transfer, and storage of cryptocurrencies use strings of numbers and letters called tokens (tokenization is a type of encryption). In cryptocurrency transactions, tokens are created and sent through the internet when transactions are created and exist as entries on a given coin’s blockchain / ledger.
- Meanwhile, sometimes when people say “token” they are specifically referring to digital assets that are built on another cryptocurrency’s platform like Ethereum’s ERC-20 tokens, ERC-223, ERC-721, and ERC-777 tokens. The native token on the Ethereum platform is Ether, 0x for example is a ERC-20 token created from the 0x ICO. Both Ether and 0x are cryptocurrencies (AKA tokens) on the Ethereum network, but one might refer to 0x as “a token” to differentiate it from the native cryptocurrency on a platform / network / blockchain.
- Token can also be used to describe “utility tokens” which are strings of data that can be used for specific functions in specific systems (such as a token that lets you access a certain amount of cloud storage).
- Token can also be used to describe “security tokens” which are strings of numbers and letters used in computer security (encrypted strings of numbers and letters). TIP: Security tokens used in computer security should to be confused with an Ethereum-based ICO tokens that might be considered financial securities in the eyes of the SEC.
Summary
In summary, tokens can be value tokens (tokens like Bitcoin), security tokens (tokens used for computer security), or utility tokens (tokens that have use values not just exchange values). In all cases we are talking about a cryptographic string of numbers of letters and the difference between value tokens, security tokens, and utility tokens is found in what the token is used for.
Semantically, in terms of discussing cryptocurrency in general, the term “token” is typically either 1. used to describe any cryptocurrency or a unit of value of a cryptocurrency or 2. used to describe ICO tokens, especially tokens on a network like Ethereum’s. I.e. “token” is synonymous with “cryptocurrency” or “cryptocurrency token.”
Meanwhile, in cases where encryption is being discussed directly, the term “token” generally is referring to an encrypted string being used as something other than a cryptocurrency.
In other words, the term “token” generally means a bunch of different things in cryptocurrency, but can mean any of the above in specific contexts.
The reality is in cryptocurrency one could be discussing any of the above due to tokenization being at the heart of so many aspects of cryptocurrency. Still, if someone says the word token in cryptocurrency… you can generally assume they are using it as a placeholder for “cryptocurrency token.”
Long answer: Not only does “token” refer to both a cryptocurrency token or a token like ETH specifically, it is also relates to the way crypto works, computer security, and a theory of how money works. In short, it is a simple term that is chalk full of meaning and thus one has to pay attention to the context in which the term is used… especially when discussing cryptocurrency as it relates to economics and computer security.
Tokens in General and in Cryptocurrency
For the first part of the page we focused on how everything applied to cryptocurrency and discussed encryption a little bit, below we will focus on how tokenization is used in cryptocurrency.
The concept of the term token in general: Generally speaking, the term “token” describes something that is a stand-in for something else.
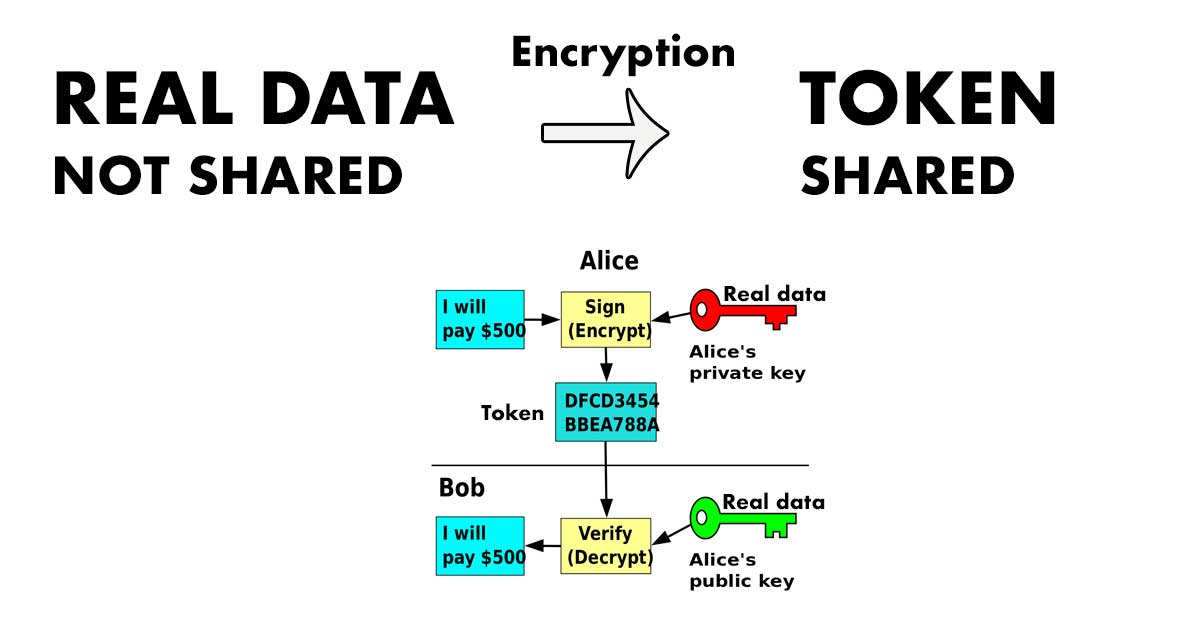
The concept of the term token in cryptography: A token is an encrypted string that relates back to data. Tokenization is simply a type of encryption (a type used liberally in cryptocurrency technology).
Tokens in computer security: In terms of computer security, a “token” is a type of encrypted data where an algorithmically generated string of data acts as a stand-in for the original data. This avoids having to send even an encrypted version of real data across the internet. The concept being that the token relates back to real data, it doesn’t contain real data. Many digital payment systems and other types of digital systems use this type of token, including Apple Pay, Square, Credit Card companies, and cryptocurrencies.[5]
The concept of a token and currency/value/money tokens: A currency token (or value token or money token) is representative of an amount of a currency (or more generally value or money), be it a dollar bill in digital or paper form, which represents $1, or a Bitcoin which represents 1BTC worth of value. Thus, both dollars and cryptocurrencies are currency tokens / value tokens / token money in this sense (they represent value and can be used as currency / money; but aren’t themselves inherently of value beyond their exchange value).
The concept of utility tokens: Not every token needs to be a stand-in for currency/value/money. Tokens can also be used in other ways. For example, Filecoin‘s tokens provide users with access to a decentralized cloud storage platform (in this respect some tokens work as coupons or tickets for x amount of a certain good or service). Being a currency is a utility, but in theory not every utility has to revolve around trade and value.[6]
ERC-20 Tokens (and other such tokens): “Token” has another meaning in cryptocurrency specifically. People often also use the term “token” to describe altcoins (cryptocurrency alternatives to Bitcoin) that exist on another coin’s platform instead of existing on their own platform. Ethereum and NEO have tokens of this type, as do other platforms. Most commonly then, here using the most popular of these platforms Ethereum as an example, “token” would refer to any ERC-20 tokens built on the Ethereum platform that aren’t the native token Ether (or any NEO-based tokens that aren’t NEO, etc).
Again, in cryptocurrency, the term “token” general refers to all these things at once… and does so somewhat loosely.
NOTE: One-way cryptographic hash functions are used to create tokens. A hash function takes any amount of data and then creates an encrypted fixed length string of data. In general, cryptocurrency uses cryptographic hash functions for many things, including the creation of tokens.
Tokens in Cryptocurrency in Terms of Encryption
In cryptocurrency, in terms of encryption, a “token” or “cryptocurrency token” is tokenized data relating to transactions that can be sent across the internet and stored (for example on a blockchain) without jeopardizing sensitive data.[7]
The idea being that each token is unique and corresponds to important data used to create a transaction (like a private key), but doesn’t contain that data specifically (so it can be shared publicly without jeopardizing the information). It is “a hash of the transaction” (and thus is a unique code that relates back to a specific transaction without containing sensitive information about it).
This allows people to confirm ownership of Bitcoin on the public ledger (aka the blockchain; which is public record), without sharing sensitive information.
The result is that the Blockchain is full of tokens of this type sitting next to public transaction data. A token (of the encrypted type) identifies the transaction and is created by the sender automatically, and the rest of the transaction data is recorded along with it.
Since the token identifies a transaction, it is used as a transaction number and is called a “TXID” (that is, a transaction ID).
It looks somethign like this:
TXID (hash of the transaction; a unique transaction ID number): 947153d332beaf39dec6ebae8883bfb84eda47abccccbc2d61436d8d1e81584d <—- this is what tokens look like
FROM (a hash of the sender’s public key; their public address): 1JMk91gy6MUBuySoxoArB6MtyeNhhSa7dr- 0.0000596 BTC
FROM (a hash of the sender’s public key; their public address): 17JvnxVuxmxYfrtJvdedhxjL8XrSF8tYqV – 0.02451455 BTC
TO (a hash of the recipient’s public key; their public address): 39fiTiMqHKToAfC4tZK2jhTzxenE7VhQMi – 0.02451681 BTC
FEE: 0.00005734 BTC
The first string is the TXID token created when a transaction is created, the next three are public addresses which relate to balances, next is the fee paid to send the transaction, and everything that isn’t plain text or a balance of BTC is a hash.
In cryptocurrency, the “token” people are generally referring to when they say “token,” is one described above PLUS the the concept of a currency token / value token.
In a way the term is being used loosely, as people aren’t saying “oh look, I own a TXID.” They mean, I own the rights to the Bitcoin as denoted on the ledger (as confirmed by my knowledge of the private keys which provided the signature which created the TXID, which relate back to the wallet address, which relates back to transactions on the blockchain).
TIP: The TXID token isn’t the only token used in cryptocurrency. Each block contains a timestamp token for example. Meanwhile, a Bitcoin address can be described as “a token.” Bitcoin is encrypted six ways from Sunday, lots of hashes are created, some hashes are also well described as tokens, and then on top of that Bitcoin is a token of value. Lots of token going on, so people tend to refer to cryptocurrencies as tokens (thereby sort of giving the term an additional meaning in general in cryptocurrency).
TIP: As you can see above, when a transaction is sent some information is encrypted and other information isn’t. A token is sent along with public addresses and amounts sent. The token is like a unique identifier for the transaction. To see a visual of this, see: //blockexplorer.com/.
The Bottomline
In cryptocurrency the term token doesn’t mean one thing, it refers to many things at once. In all cases, a token is “a stand-in for something else.”
A token is an encrypted string of data that points to data without actually containing the original data. And in cryptocurrency specifically, a token is an encrypted string of data that gets created when a person creates a transaction. This string identifies the transaction and is generally stored on the blockchain… so people sometimes call cryptocurrencies “tokens.”
In this respect Ether is the native cryptocurrency token to the Ethereum blockchain and Bitcoin is the native cryptocurrency token to the Bitcoin blockchain (where a blockchain is a digital ledger of transactions, and those transactions are tokenized and added to the blockchain as tokens).
What is the difference between a cryptocurrency and a token: Essentially there is no difference between a cryptocurrency and a token on one level, as the term token generally describes any cryptocurrency. There is only a difference in term of semantics when people use the term token to refer to security tokens specifically or specifically to tokens built on another platform like ERC-20 tokens on the Ethereum platform.
A Re-Summarization of Tokenization
Here are a few other points that will help you understand everything “token” means:
- To re-summarize the above, a token describes cryptocurrency in general and refers to the fact that cryptos are both value tokens and use strings of data called tokens.
- In computer security, a token is a type of encrypted data that allows only a encrypted token that leads back to the original data (but not the original data) to be sent and stored, cryptocurrency tokens are simply tokens that represent transactions to be recorded on a digital ledger called a blockchain, and sometimes the term token is used to describe tokens that exist on a blockchain that aren’t the native token (for example, ERC-2o tokens on the Ethereum network).
- If you just sent unencrypted data across the internet it would not be secure. So instead of doing that, information is encrypted. One method of encryption is “tokenization.” A tokenized string of data can then be sent and stored securely. Credit card companies tokenize data, email tokenizes data, Square, Apple, Google, and PayPal tokenize data, almost all computer security involves the tokenization of data, cryptocurrency tokenizes data, two factor authentication uses tokens, you see tokens in URLs when you are doing online shopping, etc. In cryptocurrency specifically, much of the data sent between public addresses via wallets and stored on the blockchain is tokenized data.
- End-to-end encryption encrypts data at the origin and then decrypts it at its destination. Tokenization encrypts data at one point and then leaves it encrypted (it is one-way encryption). Both are types of encryption, but tokenization has a specific meaning. With tokenization the data stored and sent is never stored or sent in its real form, it is always stored and sent in a tokenized (encrypted) form. With end-to-end, the real data is sent in an encrypted form, but then can be deciphered at the end point.[8]
- All cryptocurrencies can be referred to as cryptocurrency tokens, and the terms coin, cryptocurrency, and token can all be used interchangeably (although, see the next point). Do you own a digital asset? Then you can say you have X balance of X token.
- Even though the last point is true, that the terms token and cryptocurrency can be used interchangeably, a cryptocurrency is more than just a token. Firstly, a cryptocurrency is a digital ledger of transaction data (which in with most cryptocurrencies is called a blockchain). Secondly, a cryptocurrency is the encrypted transaction data (the tokenized transaction data) that gets sent between peers and added to the ledger. Third, there is more than one type of token created in the process of sending and storing cryptocurrencies.
In other words, there is a lot of tokenization going on in cryptocurrencies, and understanding each type of token means going through the Bitcoin and Ethereum wikis and picking apart each aspect of how cryptocurrencies work (where you’ll find pages on token contracts, time stamp tokens, transaction tokens, and even the concept of money).
For more information on this specific type of tokenization common to payment systems from Square, to Apple Pay, to Bitcoin see Square’s “Payment Tokenization Explained.”
BOTTOMLINE ON TOKENIZATION: With tokenization real sensitive data is never sent or stored, only an algorithmically generated number called a token is sent and stored. Thus, in cryptocurrency private data that shouldn’t be public is never directly stored on the blockchain or sent through the internet, only tokens that correspond to the original data are sent and stored. This method of encryption is common with with cryptocurrency and many payment systems like Square, Credit Card companies, and Apple Pay for example.
- An Introduction to the Bitcoin System. PascalPares.Gitbooks.io
- Token money. Wikipedia.com
- Token. Bitcoinwiki.org
- ERC20 Token Standard. Theethereum.wik
- Payment Tokenization Explained. Squareup.com.
- ICO 101: Utility Tokens vs. Security Tokens. Strategiccoin.com.
- A gentle introduction to digital tokens. Bitsonblocks.net.
- Tokenization Vs. End-to-End Encryption: Experts Weigh in